You are here
Building Blocks - Higher Order Processes

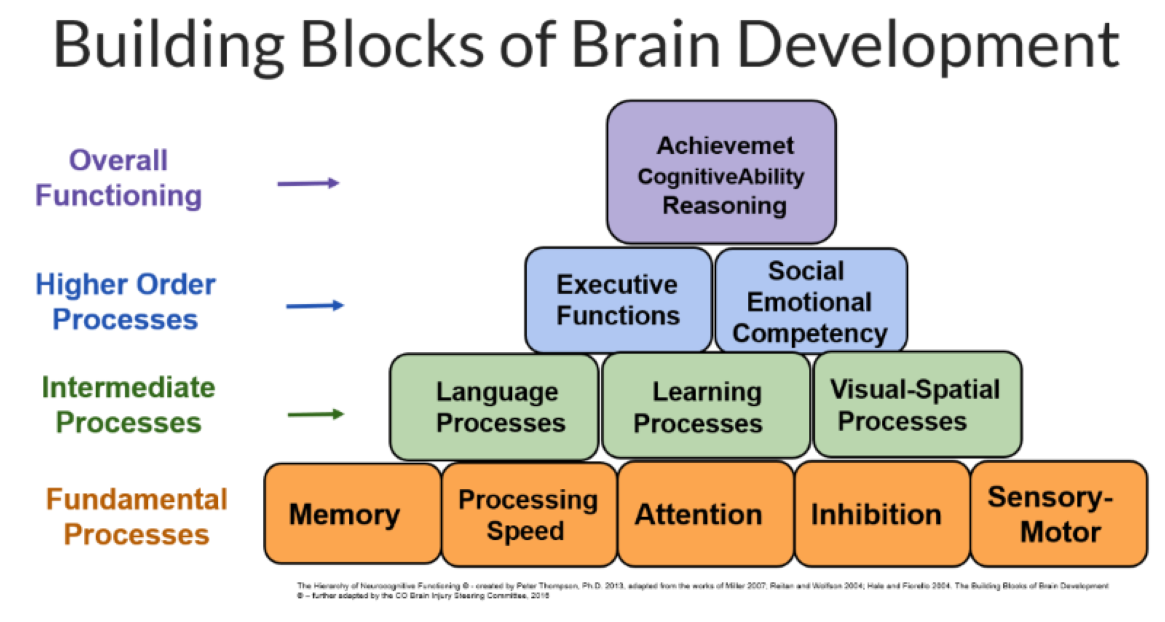
The higher order thinking skills – executive function and social emotional competency are represented at the blue level.
Executive Function - Initiation
Behavioral Impacts
- Difficulty starting tasks independently
- Can state what they are supposed to do but does not get started
- Slow to shift at same time as peers
- Requires constant cueing
- Does not make plans academically or socially
- Appears aloof or disinterested in peers
- Follower
- Lagging in independent living skills
- May appear lazy, unmotivated or spacey
- Often gets overlooked because they are not trouble in the classroom
- Seeks out adults for social interaction
Cognitive Academic Impacts
- Appears passive/resistant
- Difficulty knowing how to get started
- Difficulty managing long-range projects
- Does not complete homework or seatwork
- Turns in poor quality work
- Woefully incomplete work
Assessment Suggestions
- Behavior Rating Inventory of Executive Function, 2nd (BRIEF2)
- Comprehensive Executive Function Inventory (CEFI)
- Delis Rating of Executive Function (D-REF)
- Neurocognitive Evaluation Form
- Observations in the environment
- Behavior observations during testing
- Parent, Teacher and Student Interviews
Environmental Supports and Accommodations
- Brain Injury in Children and Youth: A Manual for Educators (Chapter 3)
- Provide a written routine to assist/help student begin work
- Provide assistance with getting started with school work
- Provide more frequent check-ins to ensure student is completing work
- Teach students how to observe others to identify what to do next
- Use visual imagery to practice the activity steps prior to initiation
- May need friendship groups or support initiating social interactions
- See Planning and Organization Building Blocks
Resources and Interventions
- Brain Injury in Children and Youth: A Manual for Educators (Chapter 3)
- BrainSTARS Chapter 3 and Blue tabbed section: #7 Initiation
- Executive Function in Children and Adolescents, 2nd (Dawson/Guare)
- Late, Lost and Unprepared (Cooper-Kahn/Dietzel)
- Promoting Executive Function in the Classroom (Meltzer)
- Smart but Scattered (Dawson/Guare)
- Smart but Scattered Teens (Guare/ Dawson/Guare)
- Tools for Teaching, 3rd (Jones)
- BrainLine Kids
- Center on Brain Injury Research & Training
- Project LEARNet
Executive Function - Planning
Behavioral Impacts
- Difficulty with problem solving
- Doesn’t make plans with friends
- Rigidity of thinking
- Often late for class
- Often unprepared for class
Cognitive Academic Impacts
- Difficulty organizing thoughts
- Difficulty with long term assignments
- Difficulty with sequential tasks
- Difficulty with time management
- Difficulty writing papers
- Doesn’t brainstorm
Assessment Suggestions
- Cognitive Assessment System, 2nd (CAS2): Planning Scale
- Kaufman Assessment Battery for Children, 2nd: Planning Ability Scale
- A Developmental Neuropsychological Assessment, 2nd (NEPSY-II): Attention and Executive Function Subtests
- Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children, 5th (WISC-V): Block Design
- Differential Ability Scale, 2nd (DAS-2): Recall of Designs and Block Design
- Behavior Rating Inventory of Executive Function, 2nd (BRIEF2)
- Comprehensive Executive Function Inventory (CEFI)
- Delis Rating of Executive Function (D-REF)
- Delis-Kaplan Executive Function System (D-KEFS): Tower Test
- Trails Making (A&B)
- Rey-Osterrieth Complex Figure
- Neurocognitive Evaluation Form
- Observations in the environment
- Behavior observations during testing
- Parent, Teacher and Student Interviews
Environmental Supports and Accommodations
- Brain Injury in Children and Youth: A Manual for Educators (Chapter 3)
- Develop, teach and reinforce schedules and routines
- Directly teach and model step by step problem solving
- Anticipate and prepare for transitions
- Report and Talk Aloud
- Check In/Check Out
- Block & Box (Sara Ward)
- The Working Clock – Time Management Strategy (Sarah Ward)
- Get Ready, Do, Done (Sarah Ward)
- Provide student with “Planning Sheet” (see Executive Skills in Children and Adolescent resource book)
- Use a smartphone and set reminders and alarms
- Teach goal-directed problem solving process
- See Initiation and Organization Building Blocks
Resources and Interventions
- Brain Injury in Children and Youth: A Manual for Educators (Chapter 3)
- BrainSTARS Chapter 3 and Blue tabbed section: #15 Planning
- Executive Function in Children and Adolescents, 2nd (Dawson/Guare)
- Late, Lost and Unprepared (Cooper-Kahn/Dietzel)
- Promoting Executive Function in the Classroom (Meltzer)
- Smart but Scattered (Dawson/Guare)
- Smart but Scattered Teens (Guare/ Dawson/Guare)
- Games that build planning abilities: Center on the Developing Child
- Software programs – e.g., “Kidspiration” (Grades K-5) and “Inspiration” (Grades 6-Adult) -developing “visual thinking”, graphic organizers, etc.
- BrainLine Kids
- Center on Brain Injury Research & Training
- Project LEARNet
- Sarah Ward Strategies
Executive Function - Organizational Skills
Behavioral Impacts
- Seems confused
- Copies behaviors of others
- Difficulty with transitions
- Easily frustrated
- Resistant
- Follower
- Is disorganized
- Loses things easily
- Spacey
- Conversations may be disjointed
Cognitive Academic Impacts
- Difficulty with long range projects
- Unable to do more than one step on a task
- Doesn’t turn in homework
- Homework is incomplete
- Not independent learner
- Often forgetful
- Work is messy
- Difficulties answering open-ended questions
Assessment Suggestions
- Behavior Rating Inventory of Executive Function, 2nd (BRIEF2): Organization of Materials and Planning/Organization Scale (look at specific items)
- Comprehensive Executive Function Inventory (CEFI)
- Neurocognitive Evaluation Form
- Observations in the environment
- Behavior observations during testing
- Parent, Teacher and Student Interviews
Environmental Supports and Accommodations
- Brain Injury in Children and Youth: A Manual for Educators (Chapter 3)
- Establish daily routine
- Check in/Check out system
- Color code subjects
- Provide student with step-by-step instructions
- Report and Talk Aloud strategy
- Smartphone apps: clock/timer, calendar with reminders, Evernote recordings/pictures/detailed instruction
- Use of classroom websites with posted notes and assignments
- Multiple small storage bins; label storage area contents – create routines for use
- Support between home and school to implement an organization system
- Teach/support organization skills/systems (folders, planners, etc.)
- Use of graphic organizers
- Use a “zipper” folder containing sections for each subject and sections for work “to do”, “completed” etc.
- Teach goal-directed problem solving process
- See Initiation and Planning Building Blocks
Resources and Interventions
- Brain Injury in Children and Youth: A Manual for Educators (Chapter 3)
- BrainSTARS Chapter 3 and Blue tabbed section: # 14 Organization, #15 Planning
- Executive Function in Children and Adolescents, 2nd (Dawson/Guare)
- Late, Lost and Unprepared (Cooper-Kahn/Dietzel)
- Promoting Executive Function in the Classroom (Meltzer)
- Smart but Scattered (Dawson/Guare)
- Smart but Scattered Teens (Guare/ Dawson/Guare)
- Tools for Teaching (Jones)
- BrainLine Kids
- Center on Brain Injury Research & Training
- Project LEARNet
- Sarah Ward Strategies
Executive Function - Mental Flexibility
Behavioral Impacts
- Argumentative
- Concrete thinker
- Rigid thinker
- Perseveration
- Difficulty making friends
- Difficulty taking feedback
- Difficulty with transitions
- Doesn’t like to try new things
- Lacks empathy
- Stubborn
- Issues with understanding the perspective of others
Cognitive Academic Impacts
- Difficulty coming up with solutions
- Difficulty deviating from schedule
- Difficulty shifting between tasks or ideas
- Difficulty with abstract thinking
- Doesn’t do what asked
- Doesn’t learn from mistakes
- Doesn’t think well on his/her feet
Assessment Suggestions
- A Developmental Neuropsychological Assessment, 2nd (NEPSY-II): Attention and Executive Function Subtests
- Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children, 5th (WISC-V): Picture Concepts, Matrix Reasoning, Comprehension (questions requiring multiple responses)
- Differential Ability Scale, 2nd (DAS-2): Matrices
- Woodcock Johnson, 4th (WJ-IV) Test of Cognitive Abilities: Concept Formation
- Delis-Kaplan Executive Function System (D-KEFS): Sorting, Trail Making, Verbal Fluency, Design Fluency, Color-Word Interference, Tower
- Wisconsin Card Sort Test
- Children’s Category Test
- Behavior Rating Inventory of Executive Function, 2nd (BRIEF2): Shift Scale
- Comprehensive Executive Function Inventory (CEFI): Flexibility Scale
- Neurocognitive Evaluation Form
- Observations in the environment
- Functional Behavioral Assessment
- Behavior observations during testing
- Parent, Teacher and Student Interviews
Environmental Supports and Accommodations
- Brain Injury in Children and Youth: A Manual for Educators (Chapter 3)
- Develop, teach and reinforce routines
- Block & Box (Sarah Ward)
- Explicitly teach flexible thinking skills (i.e., warnings, counting down time, timers, practice changing schedule)
- Guided Self-Reflection
- Plan for situations that require mental flexibility
- Teach Stop, Relax and Think
- Teach coping strategies, belly breathing, mindfulness, meditation, relaxation techniques
- Social skills groups. Teach perspective taking
- Use of social narratives
- See Reasoning and Social/Emotional Competency Building Blocks
Resources and Interventions
- Brain Injury in Children and Youth: A Manual for Educators (Chapter 3)
- BrainSTARS Chapter 3 and Blue tabbed section: #10 Mental Flexibility
- Collaborative Problem Solving (Greene/Ablon)
- Executive Function in Children and Adolescents, 2nd (Dawson/Guare)
- Explosive Child (Greene)
- Lost at School (Greene)
- Promoting Executive Function in the Classroom (Meltzer)
- Smart but Scattered (Dawson/Guare)
- Smart but Scattered Teens (Guare/ Dawson/Guare)
- BrainWise (Barry)
- The Incredible 5 Point Scale (Buron/Curtis)
- Superflex: A Superhero Social Thinking Curriculum (Winner)
- You are a Social Detective (Winner)
- Why Try (Moore)
- Zones of Regulation (Kuper)
- Games that build Mental Flexibility: Center on the Developing Child
- BrainLine Kids
- Center on Brain Injury Research & Training
- Project LEARNet
Executive Function - Reasoning
Behavioral Impacts
- Acts without thinking of the consequences
- Does not follow through with request to complete tasks
- Doesn’t think well on his/her feet
- Followers
- Lacks common sense
- Makes poor behavioral and social choices
- May appear depressed
- Oppositional
- Poor social judgment and risk taking behaviors e.g. promiscuity, school suspension
- Argumentative
- Stubborn
- Does not learn from mistakes
Cognitive Academic Impacts
- Can do rote learning but does not get broader concepts
- Concrete thinker
- Difficulty responding to open-ended or essay questions
- Difficulty with comprehension, e.g. reading, math, written expression
- Difficulty with math word problems
- Does better on multiple choice tests
- Does not generalize information appropriately (over or under generalizes)
- Does not get the big picture
- Lacks insight
Assessment Suggestions
- Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children, 5th (WISC-V): Fluid Reasoning Index, Picture Concepts, Arithmetic
- Cognitive Assessment System, 2nd (CAS2): Simultaneous Processing Scale
- Differential Ability Scales, 2nd (DAS-II): Nonverbal Reasoning Composite
- Kauffman Assessment Battery for Children (KABC-II): Simultaneous Processing Ability Scale
- Woodcock Johnson, 4th (WJ-IV), Test of Cognitive Abilities: Number Series, Concept Formation, Visualization, Analysis-Synthesis
- Test of Problem Solving, 2nd Ed Adolescent (TOPS-2)
- Test of Problem Solving, 3rd Ed Elementary (TOPS-3)
- Delis-Kaplan Executive Function System (D-KEFS): Sorting, 20 Questions, Word Context, Proverb
- Behavior Rating Inventory of Executive Function, 2nd (BRIEF2): Monitor Scale
- Comprehensive Executive Function Inventory (CEFI): Monitoring Scale
- Neurocognitive Evaluation Form
- Observations in the environment
- Functional Behavioral Assessment
- Parent, Teacher and Student Interviews
Environmental Supports and Accommodations
- Brain Injury in Children and Youth: A Manual for Educators (Chapter 3)
- Present information in concrete and concise manner
- Asking “why” questions
- Avoid sarcasm
- Scaffolding
- Inquiry-based/Cooperative Learning
- Teaching into meaningful concepts
- Use multiple choice instead of essay test formats
- Provide choices of activities or more support during unstructured times
- Teach problem-solving strategies
- Explore pros and cons of real-life situations
- Social skills groups
- Be clear and consistent on consequences of risk-taking behaviors
- See Reasoning and Social/Emotional Competency Building Blocks
Resources and Interventions
- Brain Injury in Children and Youth: A Manual for Educators (Chapter 3)
- BrainSTARS Chapter 3 and Blue tabbed sections: #8 Judgment, #12 New Learning, #13 Non-Verbal Learning, #20 Social Skills
- Executive Function in Children and Adolescents, 2nd (Dawson/Guare)
- Helping the Child who Doesn’t Fit In (Nowicki/Duke)
- Lost at School (Greene)
- Promoting Executive Function in the Classroom (Meltzer)
- BrainWise (Barry)
- Bully Proofing Your School (Garrity/Bonds/ Camilli)
- Circle of Friends
- The Incredible 5 Point Scale (Buron/Curtis)
- Skill Streaming (McGinnis)
- Superflex: A Superhero Social Thinking Curriculum (Winner)
- Why Try (Moore)
- Zones of Regulation (Kuper)
- BrainLine Kids
- Center on Brain Injury Research & Training
- Project LEARNet
Social/Emotional Competency
Behavioral Impacts
- Difficulty keeping and making friends
- Difficulty reading social cues
- Difficulty with anger management
- Emotionally labile
- Meltdowns
- Over/under reaction
Cognitive Academic Impacts
- Cognitive distortions (exaggerated or irrational thought patterns)
- Difficulty with group learning
- Emotional pre-occupation that interferes with academics
- Trouble focusing
Assessment Suggestions
- A Developmental Neuropsychological Assessment (NEPSY-II): Social Perception Subtests
- Behavior Assessment System for Children, 3rd (BASC-3)
- Emotional Disturbance Decision Tree (EDDT)
- Scales for Assessing Emotional Disturbance, 2nd (SAED-2)
- Behavior Rating Inventory of Executive Function, 2nd Ed (BRIEF2): Emotional Control Scale
- Comprehensive Executive Function Inventory (CEFI): Emotional Regulation Scale
- Children’s Depression Inventory, 2nd (CDI2)
- Reynold’s Adolescent Depression Scale, 2nd (RADS-2)
- Revised Children Manifest Anxiety Scale, 2nd (RCMAS-2)
- Multidimensional Anxiety Scale for Children, 2nd (MASC 2)
- Conners, 3rd
- Conversational Effectiveness Profile – Revised (CEP-R): An assessment tool measuring Social Interaction, Social Communication, and Social-Emotional Regulation; socialpragmatics.com
- Social Skills Rating System (SSRS)
- Test of Pragmatic Language, 2nd (TOPL-2)
- School Functional Assessment (SFA)
- Vineland Adaptive Behavior Scales, 2nd (Vineland-II)
- Adaptive Behavior Assessment System, 2nd (ABAS-II)
- Functional Behavioral Assessment (FBA) Behavior observations during testing
- Neurocognitive Evaluation Form
- Observations in the environment
- Parent, Teacher and Student Interviews
Environmental Supports and Accommodations
- Brain Injury in Children and Youth: A Manual for Educators (Chapter 3)
- Give clear and simple directions
- Provide, teach and reinforce routines and clear expectations
- Provide calm down area
- Discuss and practice age-appropriate behaviors in real life situations
- Social skills groups
- Social narratives
- Teach coping strategies, belly breathing, mindfulness, meditation, relaxation techniques
- Behavior Intervention Plans
- See Inhibition, Mental Flexibility and Reasoning Building Blocks
Resources and Interventions
- Brain Injury in Children and Youth: A Manual for Educators (Chapter 3 and 4)
- BrainSTARS Chapter 3 and Blue tabbed sections: #1 Adolescent Self-Regulation, #3 Emotion Regulation, #18 Self-Regulation, #20 Social Skills
- Collaborative Problem Solving (Greene/Ablon)
- Explosive Child (Greene)
- Lost at School (Greene)
- Tools for Teaching (Jones)
- Alert Program: How Does Your Engine Run (Williams/Shellenberger)
- Aggression Replacement Training (Goldstein/Guck/Gibbs)
- BrainWise (Barry)
- Bully Proofing (Garrity)
- Circle of Friends
- In Focus (McSheehy)
- Incredible 5 Point Scale (Buron/Curtis)
- Incredible Years (Webster-Stratton)
- Make Social Learning Stick! (Sautter)
- MindUp Curriculum (Hawn Foundation)
- Positive Behavior Intervention Supports
- Project Achieve – Stop & Think Program (Knoff)
- Project Success (Kastner)
- Second Step
- Social Thinking Worksheets for Tweens and Teens (Winner)
- Skill Streaming (McGinnis)
- Superflex: A Superhero Social Thinking Curriculum (Winner)
- You are a Social Detective (Winner)
- Why Try (Moore)
- Zones of Regulation (Kuper)
View more information on Social Emotional Competency
Additional Resources
- Aggression Replacement Training. Goldstein, A, Glick, B. & Gibbs, J. Research Press
- American Speech Language Hearing Association
- Assessment and treatment of TBI with school age children & adults. 1992. Ylvisaker, M. Buffalo NY: Educom Associates
- *Brain Injury in Children and Youth: A Manual for Educators. 2018. Colorado Department of Education.
- Brain Injury Survival Kit, 365 Tips, Tools, & Tricks to Deal with Cognitive Function Loss. 2008. Sullivan, C.
- *BrainLine – Children with TBI – www.Brainline.org
- BrainSTARS: Brain Injury—Strategies for Teams and Re-education for Students. 2002. Dise-Lewis, J., Calvery, M. & Lewis, H.
- BrainWise: 10 wise ways to stop and Think 1996. Barry, P.G. Denver, CO: Innisfree Press.
- Bully Proofing Your School. 2004. Garrity. C. Longmont, CO: Sopris West.
- *The Center on Brain Injury Research & Training. Evidence-based strategies for students with Brain Injury. https://cbirt.org/back-school
- *Center on the Developing Child: Harvard University. http://developingchild.harvard.edu/resources/activities-guide-enhancing-and-practicing-executive-function-skills-with-children-from-infancy-to-adolescence/
- Circle of Friends. https://www.circleofriends.org/
- Essentials of School Neuropsychological Assessment, Second Edition. 2013. Miller, D.C. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley and Sons, Inc.
- Executive Function in Education: From Theory to Practice. 2007. Meltzer, L. NY: Guilford Press.
- Executive Skills in Children and Adolescents, 2nd Edition. 2010. Dawson, P. & Guare, R. NY: Guilford Press.
- Explosive Child: A New Approach for Understanding and Parenting Easily Frustrated, Chronically Inflexible Children. 2014. Greene, R.W. Harper Paperbacks
- Helping the Child who Doesn’t Fit In. 1992. Nowicki, S. and Duke, MP. Peachtree Publishers
- How does your engine run? Alert Program for Self-Regulation. 1996. Williams, MS. & Shellenberger, S. TherapyWorks, Inc.
- In Focus: Improving Social and Emotional Intelligence One Day at a Time. 2013. McSheehy, T. Burlington, WI: Thoughtful Learning.
- Incredible 5 Point Scale. 2012 Burone, K. D. & Curis, M. Lenexa, KS: AAPC
- Incredible Years, Incredible Years Program, Seattle, Washington http://www.incredibleyears.com/
- *Interventioncentral.org – Interventions, suggestions, tools for social/emotional strategies. www.interventioncentral.org
- Kidspiration (Grades K-5) & Inspiration (Grades 6-Adult) Software programs – http://www.inspiration.com/
- Late, Lost, and Unprepared: A Parent’s Guide to Helping Children with Executive Funtioning. 2008. Cooper-Kahn, J. & Dietzel, L. Bethesda, MD: Woodbine House, Inc.
- *LEARNet, Ylvisaker, M, HibbardM & Feeney, T. www.projectlearnet.org
- Lifeskills Training http://www.lifeskillstraining.com
- Lost at School: Why Our Kids with Behavioral Challenges are Falling Through the Cracks and How We Can Help Them. 2014. Greene, R.W. New York, NY: Scribner.
- Make social learning stick!: How to guide and nurture social competence through everyday routines and activities. 2012. Sautter, E. Shawnee Mission, KS: AAPC Publishing.
- The MindUp Curriculum: Brain Focused Strategies for Learning and Living. 2010. Hawn Foundation. New York, NY: Scholastic Teaching Resources.
- *Positive Behavior Intervention Support. https://www.pbis.org
- Project Achieve: Stop & think social skills program. 2001. Knoff, H. Longmont, CO: Sopris West.
- Promoting Executive Function in the Classroom. 2010. Meltzer. L. New York, NY: Guilford Press.
- Providing Alternative Thinking Strategies (PATHS), Kusche, C. and Greenberg, M., Channing Bete Company.
- Sarah Ward: Cognitive Connections: 360 Thinking. http://efpractice.com/
- SecondStep: Skills for Social and Academic Success. 2011. Goldstein, A & McGinnis, E. Research Press Publishers http://www.cfchildren.org/second-step SkillStreaming.
- Smart but Scattered. 2009. Dawson P & Guare R. NY: Guilford Press.
- Smart but Scattered Teens. 2013. Guare, R., Dawson, P. & Guare. New York, NY: Guilford Press.
- Social Thinking Worksheets for Tweens and Teens. 2014. Garcia Winner, M. San Jose, CA: Think Social Publishing, Inc.
- Superflex: A Superhero Social Thinking Curriculum. 2008. Madrigal, S. & Garcia Winner, M. Think Social Publishing.
- Teachers Encyclopedia of Behavior Management 100 Problems/500 Plans. 2012. Sprick, R and Howard, L. Pacific Northwest Publishing
- *Think:Kids – Rethinking Challenging Kids. Massachusetts General Hospital. http://www.thinkkids.org/
- Tools for Teaching, 3rd Edition. 2013. Jones F. CA: Frederic H Jones & Associates, Inc.
- Treating Explosive Kids: The Collaborative Problem Solving Approach. 2005. Greene, R.W. & Ablon, J.S. New York, NY: Guilford Press.
- Visual Spatial Portals to Thinking, Feeling and Movement 2012. Wieder, S., & Wachs, H. Mendham, New Jersey: Profectum Foundation
- *What Works Clearinghouse. 2002. U.S. Department of Education, Institute for Education Sciences. www.whatworks.ed.gov
- Why Try – Building Resilience in the Workplace, at School and at Home. Moore, C. https://www.whytry.org/
- You are a Social Detective. 2008. Garcia Winner, M. & Crooke, P. San Jose, CA: Think Social Publishing, Inc.
- The Zones of Regulation: A Framework to Foster Self-Regulation & Emotional Control. 2011. Kuypers, L. San Jose, CA: Think Social Publishing.
Building Blocks of Brain Development & Glossary Developers/Authors (2018): Nicole Crawford, Patricia Colella, Judy Dettmer, Heather Hotchkiss, Karen McAvoy, Peter Thompson, Janet Tyler. Special Thanks to Tami Cassel, Donna Detmar-Hannah, Laura Dosch, Jayne Dougherty, Mary Linz, and Jennifer Mathis.
Revise only with permission.
Revised Brain Injury Matrix & Glossary Developers/Authors (2015): Nicole Crawford, Patricia Colella, Donna Detmar-Hannah, Judy Dettmer, Heather Hotchkiss, Corey Klein, Karen McAvoy, Peter Thompson, Kristy Werther.
Traumatic Brain Injury Networking Team Steering Committee (TNT)-Original Developers/Authors of the Brain Injury Matrix (2012): Nicole Crawford, Judy Dettmer, Jeanne Dise-Lewis, Priscilla Hurley, Megan Koepsell, Karen McAvoy, Kathy Patrick, Peter Thompson, Liz Wilburn.

Connect With Us